
Jul 13, 2020
The Hagia Sophia is making the news these days because the Turkish president is changing the status of the great building from a world museum and UNESCO World Heritage site…to a mosque. But what is the Hagia Sophia? It’s perhaps a shame that so few understand the incredible role the Hagia Sophia basilica played in world history.
The medieval era marks one of only four major eras in human history. Historians generally classify the medieval era as lasting from 500 to 1500 C.E. Well, the Hagia Sophia fulfilled its historical role from 537 to 1453 – the exact time frame of the medieval era. Perhaps no other building exists in the Western Hemisphere that serves as a better embodiment of the medieval era than the Hagia Sophia.

OLYMPUS DIGITAL CAMERA
Many people in the world today view the St. Peter’s Basilica in Vatican City as the center of Christendom. And yet, St. Peter’s Basilica is a scant 394 years old. By comparison, Hagia Sophia is 1,483 years old. Go ahead a whistle if you’re impressed. Unlike many buildings of this vintage, the Church of Holy Wisdom, as it is alternatively called, is still fully functional.
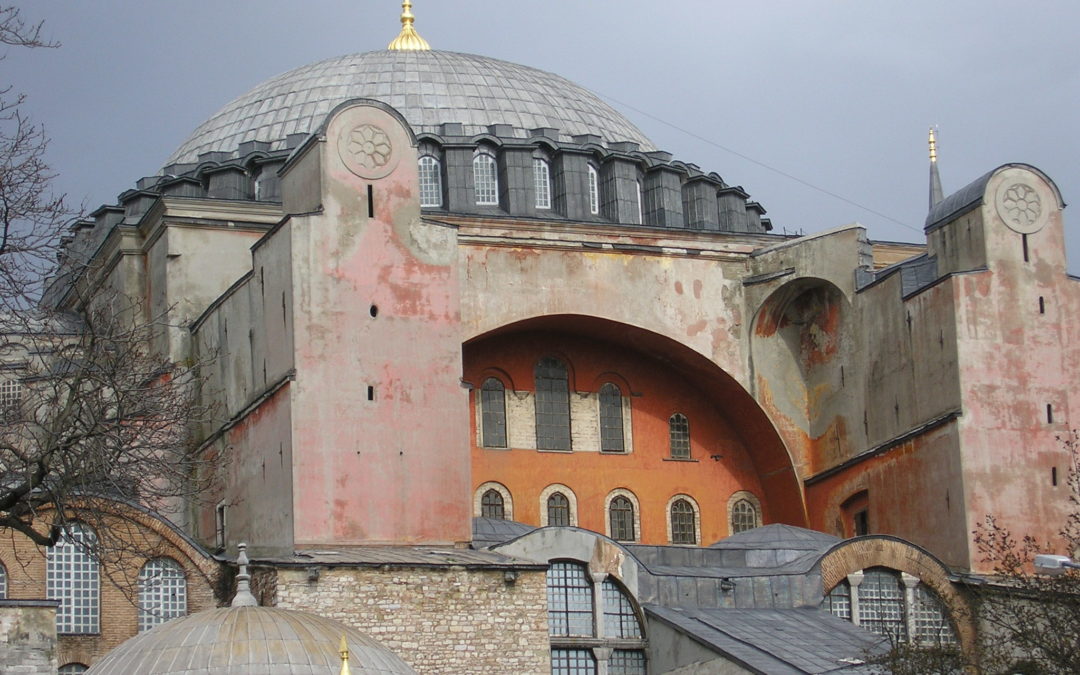
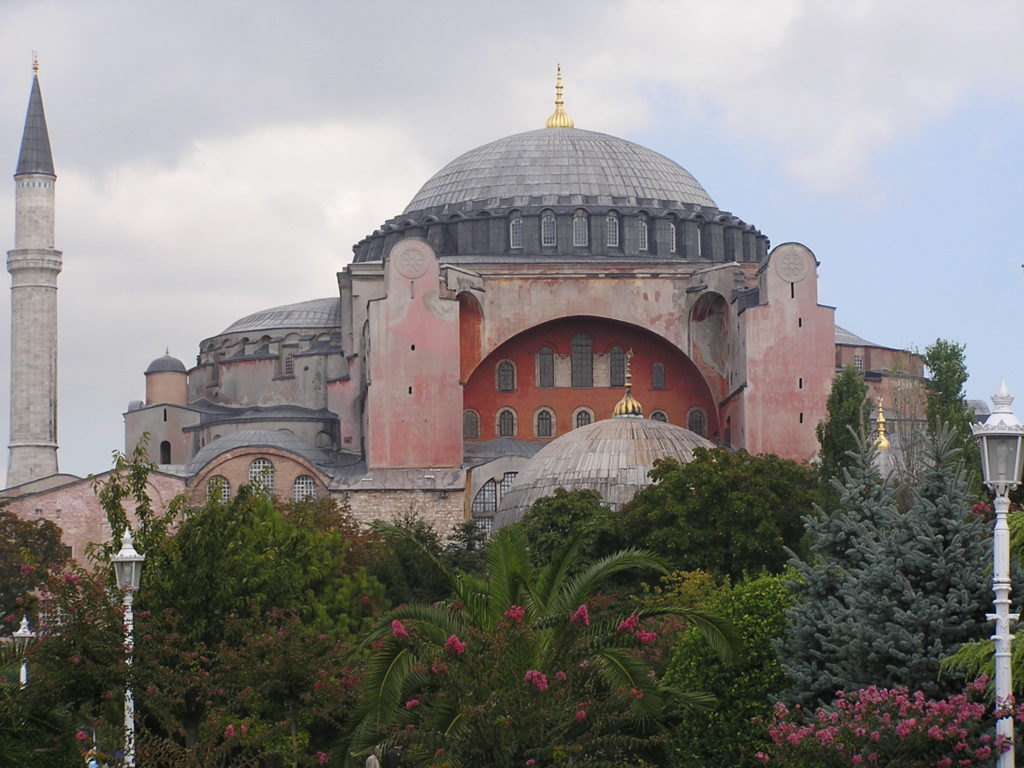
Older than Islam, the Hagia Sophia basilica had been built as the monumental symbol of Christendom on earth. The bulky structure faces out to the world with a hue of faded red paint, crowned by a purple-gray dome, and topped with a golden spike. Four minarets flank the building, two at the fore and two at the rear (these are more recent additions).

OLYMPUS DIGITAL CAMERA
Timeline of the Hagia Sophia:
532 – The original Hagia Sophia was destroyed during the Nika Riots
537 – The current architectural wonder is completed during the reign of Justinian and Theodora the Great
1204 – Converted to a Roman Catholic cathedral, after Western crusaders sack Constantinople
1261 – Returned to the Eastern Orthodox Church
1453 – Converted to a mosque after the fall of Constantinople to the Ottoman Turks
1507 – Construction of St. Peter’s Basilica begins in Italy to replace the Hagia Sophia
1616 – The Blue Mosque is built across from the Hagia Sophia in Istanbul
1626 – St. Peter’s Basilica is finally consecrated
1934 – Mustafa Kemal Ataturk, the father of modern Turkey, converts the Hagia Sophia to a museum
2020 – President Recep Ergodan, Turkey’s current leader, decreed the Hagia Sophia to be a mosque again
While Europe was slogging through a violent and regressive dark age, the Hagia Sophia rose above the city of Constantinople as a bulwark of civilization and a beacon of religious devotion that defined the era. The Hagia Sophia was the largest church in the world, with one of the largest enclosed spaces until modern times, and featuring architectural distinctions that redefined architecture.
I’ve been there. I’ve seen it. And the building is spellbinding. After passing through massive doorways once reserved for Roman emperors, you enter a cavernous space of gleaming marble, a forest of marble pillars, and a haze of foggy sunlight peeking through the windows. One gazes up into the underside of the great dome and falls dizzy with wonder.
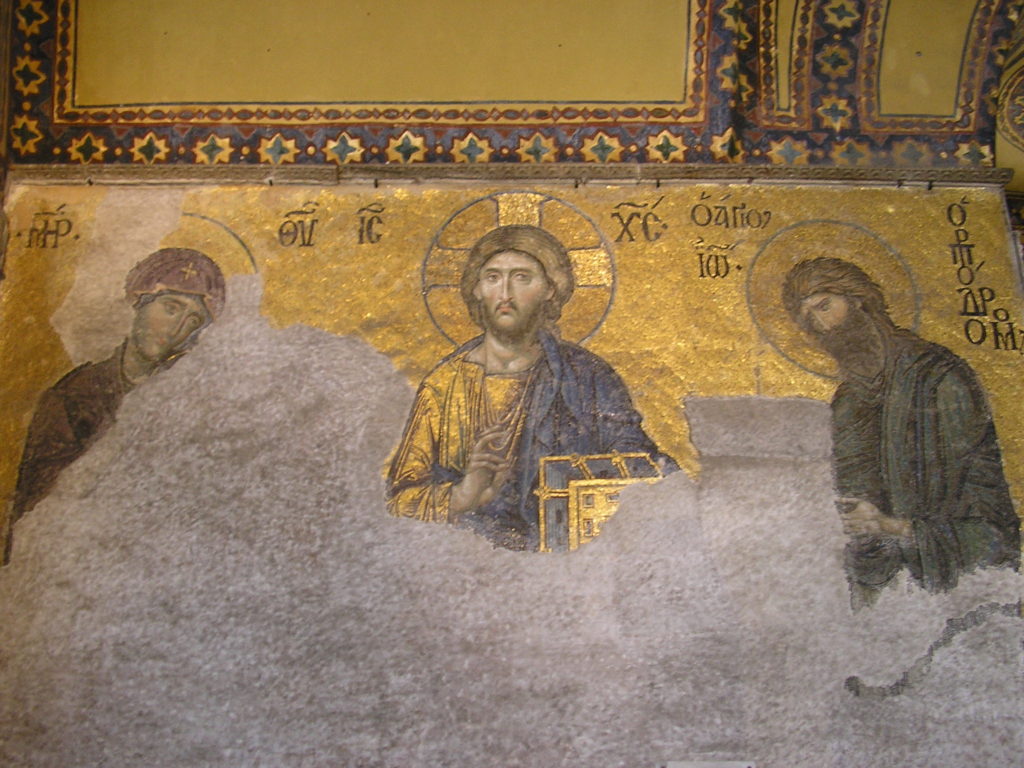
In my opinion, the Western world doesn’t give enough credit to the Greek-speaking Byzantine Empire that built the Hagia Sophia. Clearly, we took for granted that such an important site wouldn’t be nationalized at the snap of one man’s fingers. And since human depictions are not allowed within mosques, the stunning historical mosaics that adorn the walls will likely be covered up with plaster or some other means. This is equivalent to covering up the ceilings of the Sistine Chapel.

OLYMPUS DIGITAL CAMERA
The Hagia Sophia should remain a museum. A museum is a higher calling since it preserves something about all human history, regardless of religion or nation or politics. It’s universal and inclusive. A museum belongs to all of us and enlightens us. If you suspect that perhaps you don’t know much about the Byzantine Empire, please explore. It’s fascinating. The Byzantines set the table for the modern world in ways you may not have suspected.
History matters. And we must never forget.
Douglas A. Burton is an author of historical fiction. His critically-acclaimed and award-winning novel, ’Far Away Bird’ follows the early life of Byzantine Empress Theodora. Doug has been on a mission to introduce the Byzantine Empire’s vital role in history and Empress Theodora’s vital contribution to women’s rights.
Further reading:
Empress Theodora: Origins of Women’s Rights
History’s Greatest Cover-up: The Byzantines

Feb 5, 2020
There are many currents that flow into our modern understanding of women’s rights. Many cultures have recognized for various levels of egalitarian or matriarchal traditions and we have countless examples of great women in power—from the pharaoh Hatshepsut to Queen Victoria to Eleanor Roosevelt. But one woman—Empress Theodora— achieved such a decisive victory for women in her time that her relative obscurity is breathtaking. Her legacy lives on today, though you may not know it.
More than fifteen hundred years ago, Theodora helped influence massive legal reforms aimed at improving the plight of women. During her reign, she influenced parts of a legal codex known as the Corpus Juris Civilis, which included a wave of specific rights for women. Historians credit this body of Byzantine law as central source material to the legal tradition of Western civilization. Whoa. That means Empress Theodora made direct contributions that survive today in the legal systems of the American Constitution, English common law, and even international public law. It’s rare to see such advanced legalism in the early Medieval era, but rarer still to know the individual woman behind the endeavor.
But just who is Empress Theodora? What laws did Empress Theodora change? And why don’t more people know about her?
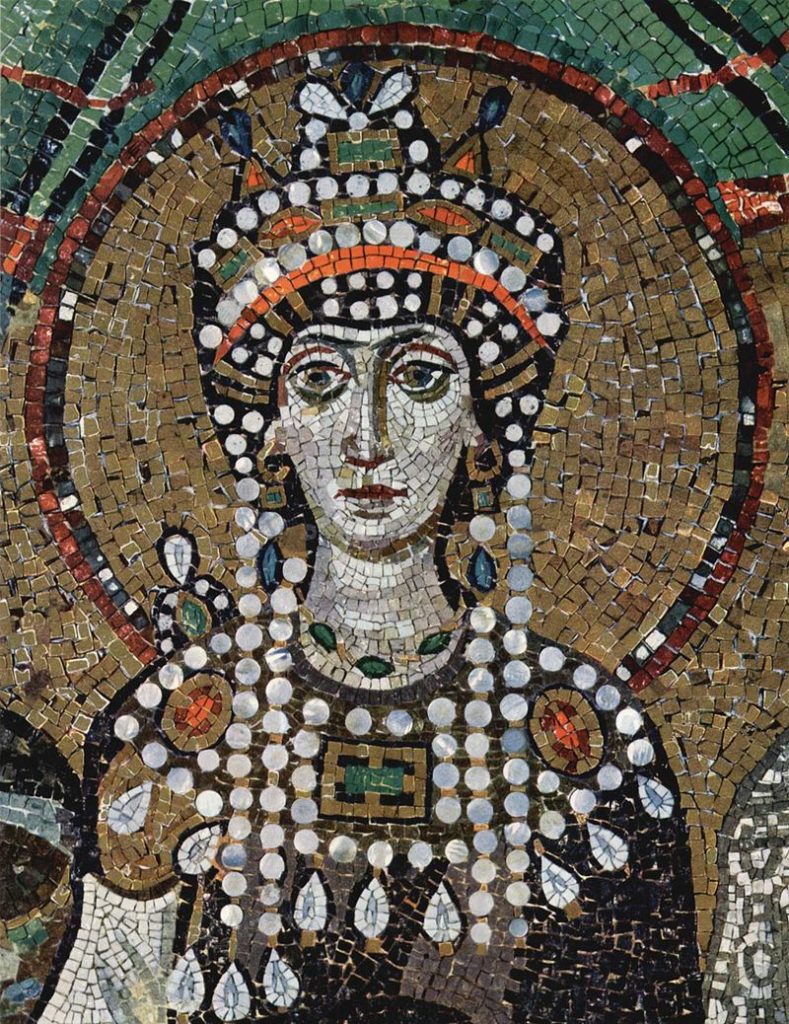

Portrait mosaic in the Basilica of San Vitale, Ravenna
“That means Theodora made direct contributions that survive today in the legal systems of the American Constitution, English common law, and even international public law.”
Abandoned by most Western thinkers throughout the centuries, Empress Theodora came off as a salacious novelty, a Medieval prostitute-stripper who made it to the top through a lucky marriage. The scandalous gossip[i] of her past, which is handed down to us by a single male source, Procopius of Caesarea, no doubt stirred the imaginations of Western historians through the centuries. The general consensus throughout history is that prostitutes have little historical value and make poor role models. But missing from this harsh judgment is the fact that as a prostitute, Theodora was part of an institutional system that marginalized women to an extreme. Her perspective was necessary for addressing women’s rights because she had firsthand knowledge and experience about the reality for women. She dared to articulate the specific problems women faced at a time when no one cared or listened. Even so, Theodora insisted on designing real-world solutions, defined in legal terms, to fix the problems she knew existed.
Theodora’s personal ideas and solutions became law[ii]. And she didn’t eff around about it.
Under Empress Theodora, rape was made punishable by death. This law extended to anyone present during the rape, regardless of position or rank, and the rapist’s property was even transferred to the rape victim[iii].
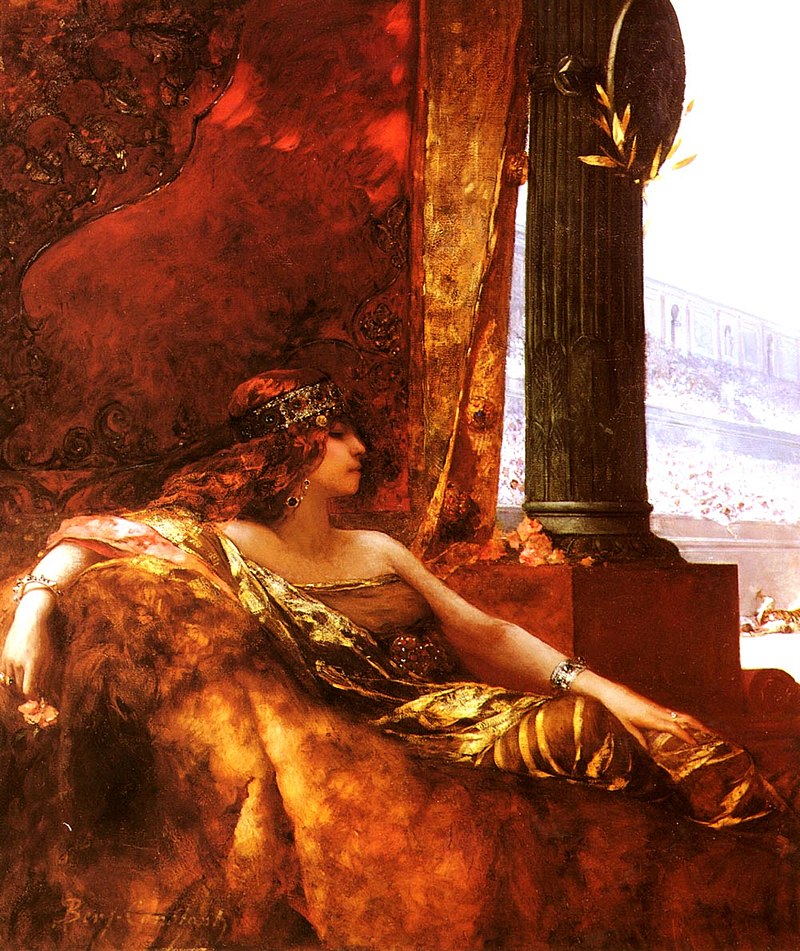

Painting by Jean-Joseph Benjamin-Constant
Theodora also saw to it that women could own and inherit property[i], which is quite a breakthrough because it gave daughters and wives real social power. A family’s wealth could now continue through a daughter, and should a woman’s husband die, the wife could claim the property and fortune. This greater legal right alone gave women throughout the empire real power in real terms.
Unlike today, professional outlets for women were severely restrictive. Besides the socially acceptable “work-from-home-and-raise-a-family” jobs, such as weaving, innkeeping, or baking, the very concept of ‘professional women’ as a large and recognizable class did not exist with one exception. A large number of women worked in theaters and brothels. So, although this professional class of women carried a huge social stigma, their industry was one of the few places where women worked publicly outside the traditional family structure and earned real income.
Therefore, laws that addressed legal matters for this lowly and socially powerless group is bold and unashamedly supportive of women in general. Theodora meant to treat the professional women of her society, sex workers though they may be, as professionals. She understood that these prostitutes, actresses, mimes, and singers earned money and could technically sustain themselves independently. But brothel keepers had legal authority over these women. So, Theodora shifted that legal authority back to women.
“These reforms should be regarded as revolutionary since they shattered the most powerful class barriers.”
Under the new laws, no woman could be forced into prostitution[i]. If a woman willingly chose prostitution, but later wished to leave the profession, Theodora’s laws made it illegal for a brothel-keeper to stop her. And Theodora followed up relentlessly to ensure enforcement of the laws. When Theodora discovered that brothel keepers undermined the new regulations by making girls swear oaths never to leave the brothels, she responded by rendering such oaths illegal[ii]. She mandated that the provincial governor and the head bishop had the responsibility to enforce this law, giving her direct oversight over a manageable number of men in high positions. She chose two men to enforce, because if the governor, himself, blocked a woman’s departure from a brothel, then the bishop could override the governor. You see, Theodora had once been a concubine in the service of one of these provincial governors. She knew only too well the kind of power these men had over women. She curbed that power at the highest levels.
And Theodora didn’t stop there. She helped to overhaul the marriage laws of her time. These reforms should be regarded as revolutionary since they shattered the most powerful class barriers.
For centuries, there was a ban on intermarriage between the upper and lower classes[iii]. By law, a prostitute could never marry a nobleman. Such a rigid class system was characteristic of a Roman world view that regarded high title and rank as self-evident. Secondly, even under the new Christian perspective, prostitution was regarded as immoral and sinful. Therefore, when Theodora helped to facilitate the removal of the marriage ban, she did so without the support of either the secular or religious tradition. Her personal world view alone guided the legal reform. By removing the marriage ban[iv], prostitutes could now marry into noble houses and gain legal status. Like it or not, this represents unparalleled social mobility for women at the time. It gave women access to power.
By having the marriage ban removed, Theodora saw to it that her sister, her daughter, and numerous other theater friends all married into noble houses. Just like that, several women crossed an impossible barrier and gained incredible social power, and they achieved this change in fortune seemingly overnight.
“Therefore, when Theodora helped to facilitate the removal of the marriage ban, she did so without the support of either the secular or religious tradition.”
Once, Theodora arranged a marriage between one of her theater friends (an ex-prostitute) and a nobleman named Saturnitus[i]. When Theodora heard that this Saturnitus complained that his prospective bride wasn’t a virgin, she had the nobleman rolled in a blanket and flogged with a cane. She asked Saturnitus just one question: why could he frequent the brothels with impunity and dare demand virginity in his wife? Theodora didn’t believe in double standards.
Other laws, too, applied to all women regarding marriage. In Byzantium, there was a law of ‘mutual consent’ in divorce cases. A divorce was granted only if both the husband and the wife agreed to void the marriage. By the way, this legal concept is still practiced in some countries today. If the wife seeks a divorce, but not the husband, she stays married against her will. You might point out that this law works in both directions. However, if a man was forced to stay in a marriage because his wife vetoed the divorce, especially back then, he could easily visit a brothel, hippodrome, amphitheater, or tavern and enjoy a full life outside the home. Wives did not have this luxury. (They weren’t even allowed on the street without a male escort[ii]). So, the law of mutual consent worked disproportionately against women.
So, Theodora had the law of mutual consent struck down.
Secondly, women of the time were expected to offer a dowry to their grooms. By Theodora’s time, the custom had expanded to make it fashionable for men to offer something minor in return. This minor offering was called an “antenupital.’ Under the new laws, the antenupital had to be equal to the bride’s dowry. Equal to the bride. Theodora’s message is consistent and clear.
She also knew that prospective brides could sometimes be pressured into a marriage. A woman might give consent initially when put on the spot, but as the marriage date grew near, she might think differently. Therefore, a new law came out that required the prospective bride to give her consent twice—once at the original proposal, and then again before the marriage took place. This allowed women to change their minds before entering into a lifelong commitment[iii].

Painting by Jean-Joseph Benjamin-Constant
Finally, in what I regard as a remarkable example of Theodora’s scope, sympathies, and real-world knowledge, she even dared to protect criminal women. In the Sixth Century, protection for male criminals wasn’t even a concern. That’s why I regard Theodora’s intervention on behalf of criminal women to be truly groundbreaking. If a woman required prison time, the new laws forbade her imprisonment in common jails where she had no protection from male guards who could abuse these women without recourse. She saw to it that criminal women were removed from common prisons and detained in a nunnery (that she constructed), under the supervision of other women.
Empress Theodora was known to hold court in her opulent imperial bedchamber. There, surrounded by a retinue of her most trusted women and eunuchs, she ruled over what has been described as an almost “parallel government[i].” Many women (and men) came directly to Theodora to plead for justice, and the formidable empress meted out justice with purpose. The scene in Theodora’s bedchambers must have mirrored the impressive throne room of the Byzantine Empire, just a few hundred feet away. In the words of James Allan Evans in his book about the empress, “In the eyes of the upper-class beholder, what Theodora represented was revolutionary.”
What’s more about this incredible woman is that she acted out her beliefs on equality. She inspired an unprecedented partnership with her husband, Justinian. Far from a great woman who ruled in the absence of a male ruler, Theodora ruled right alongside Justinian the Great, who is considered one of the greatest emperors in Byzantine history. When he addressed the Byzantine court in the throne room, Theodora sat exactly beside him, which was not typical. Theodora was free to address whomever she pleased. The emperor did not grow angry when she disagreed with him before the court. Instead, they actively debated the merits of different policies openly. She and Justinian were also faithful to each other. Their relationship was considered bizarre by their contemporaries, but I see it as a shining example for any of us. Theodora insisted on being treated as an equal, and Justinian unapologetically treated her an equal.
“The scene in Theodora’s bedchambers must have mirrored the impressive throne room of the Byzantine Empire, just a few hundred feet away.”
Theodora’s mark on history is a powerful, immovable example for us. The body of laws that came into being during her reign is known as the Corpus Juris Civilis and, according to Wikipedia: “The Corpus continues to have a major influence on public international law. Its four parts thus constitute the foundation documents of the Western legal tradition[i].” Uh, wow. If this is true…if the corpus is at the heart of the Western legal tradition, then Theodora stands front and center to the tradition of women’s rights. Official credit goes to Justinian for the Corpus, and he deserves plenty of it. But no historian can doubt Theodora’s presence in the laws that pertain to women. History, it seems, remains uncomfortable with Theodora’s sexualized past. But it’s time to recognize the crucial connection between her early life experiences and the incredible legal reforms she oversaw as an empress.
Our culture is taking a second look at history and rediscovering the many contributions of women throughout the ages. I say, look further eastward, beyond Europe, and deeper into the past. In my view, Theodora should finally take her place among the Pantheon of our greatest women in history. If Empress Theodora and her accomplishments impressed and inspired you, please share this article!
Douglas A. Burton is on a mission to introduce Theodora to everyone who admires great women of history. His award-winning novel, ‘Far Away Bird,’ which intimately details Theodora’s early life, is available now on Amazon here: Get my copy of ‘Far Away Bird’ and #MeetTheodora Or learn more at douglasaburton.com
[1] The Secret History, Procopius [9. p15]
[1] The Empress Theodora: Partner of Justinian p. 37
[1] Codex Justinianus [Book IX Title 13]
[1] Novellae 5.2 cf. Evans (1996a), pp 209-10
[1] Codex Justinianus [I.4.33]
[1] Novellae 51
[1] The Empress Theodora: Partner of Justinian p. 37
[1] Codex Justinianus (Book V Title 4-23)
[1] The Secret History, Procopius [17. p24-26]
[1] Constantinople: Birth of an Empire
[1] The Emperor Justinian and the Byzantine Empire p. 27
[1] Theodora: Empress of Byzantium p.175
[1] Wikipedia ‘Corpus Juris Civilis’

Jan 23, 2020
Here’s a fun little test. Name a major mainstream movie, television show, or novel that has the Byzantine Empire as a setting and from the Byzantine perspective. No, really, name one.
I mean, we have movies set in ancient Greece, Ancient Egypt, Rome, Medieval Japan, Medieval China, South America, the Mayan Empire, Antarctica, Mars, Middle-Earth, and Tatooine. And yet, the vast and exotic Byzantine Empire seems to be “redacted.” Seriously. Why?
Most of our perception of Byzantine culture comes indirectly through our fascination with the mysticism of Eastern Europe. We see it in stories like Bram Stoker’s Dracula, which takes place in Romanian Transylvania and has an occultic Byzantine feel, or Agatha Christie’s Murder on the Orient Express. We see the Hagia Sophia in movies like From Russia with Love, The International¸ or Tom Hank’s Inferno. And most recently, Millennials walked on the streets of 16th Century Constantinople in the critically acclaimed video game, Assassin’s Creed: Revelations. But these are just scant traces of Byzantium in our modern culture.

(Above) Bram Stoker’s Dracula (1992). (Below) Assassin’s Creed: Revelations (2011)
For 25 years, I’ve read about the Byzantine Empire and only a few of my closest friends and family members know about my unusual side passion. Even they don’t ask “why” anymore. Whenever I do end up mentioning something about the Byzantine Empire, or that the capital was Constantinople, the most common response I get (and I’m not kidding) is a pause and then a cheery rendition of Istanbul Not Constantinople. So now it’s Istanbul, not Constantinople, and we all get that.
But how did this particular time and place in the world come to capture my imagination so entirely? Like many things for me, the culprit was a book.

I can actually tell you the exact day my fascination with the Byzantine Empire began. It was in March of 1993. I know this because the library card is still inside the book cover to this day. The book was a non-fiction work called Constantinople: Birth of an Empire by Harold Lamb, and it was published way back in 1957. During my 1993 study hall, though, I just needed a book to pass the time because I surely wasn’t going to do my Algebra homework. So, I flipped through the pages, and the musty scent of old paper really set the tone. There were some black & white pictures on a few pages depicting a mosque-like building of some kind, various mosaics, and stone reliefs. I turned back to the first page and started reading…
The author opens with:
This is the story of a city built by survivors. As often happens in a great disaster, these survivors were not one people ethnically, but a fusion of many peoples. They gathered together to defend not so much their lives and property as their way of life. In so doing, they displayed a certain perversity; they refused to surrender their city. They kept on refusing for nearly a thousand years. History has named them the Byzantines…
So, wait a minute, I thought. This sounds nothing like the Roman Empire I learned about in any schoolroom. The Romans were of one people ethnically, you know…the Romans? So, this account baffled me. The Roman Empire was a civilization built by brute conquerors, not desperate survivors.
The author goes on:
They were alone in their survival. In the West, a long twilight fell on the Roman Empire during the centuries between A.D. 200 and 450. It ended in the darkness of the first Middle Age. In the East, however, the inhabitants of this city learned the hard lessons of disaster, and they managed to hold back the night.
Images of invincible Roman legionnaires, of architectural splendor, and ancient decadence all seemed at odds with the rather morbid tone the book struck. What the hell was this guy talking about? I flipped to a map in the index and got a better idea. The Roman Empire had been split in two at some point, a west and an east empire. I remembered hearing something about the split but then also realized that I never heard about what happened to that eastern portion of the empire. It was like the weird old uncle you meet at a family reunion and never hear from again.
Here’s what I’m talking about:
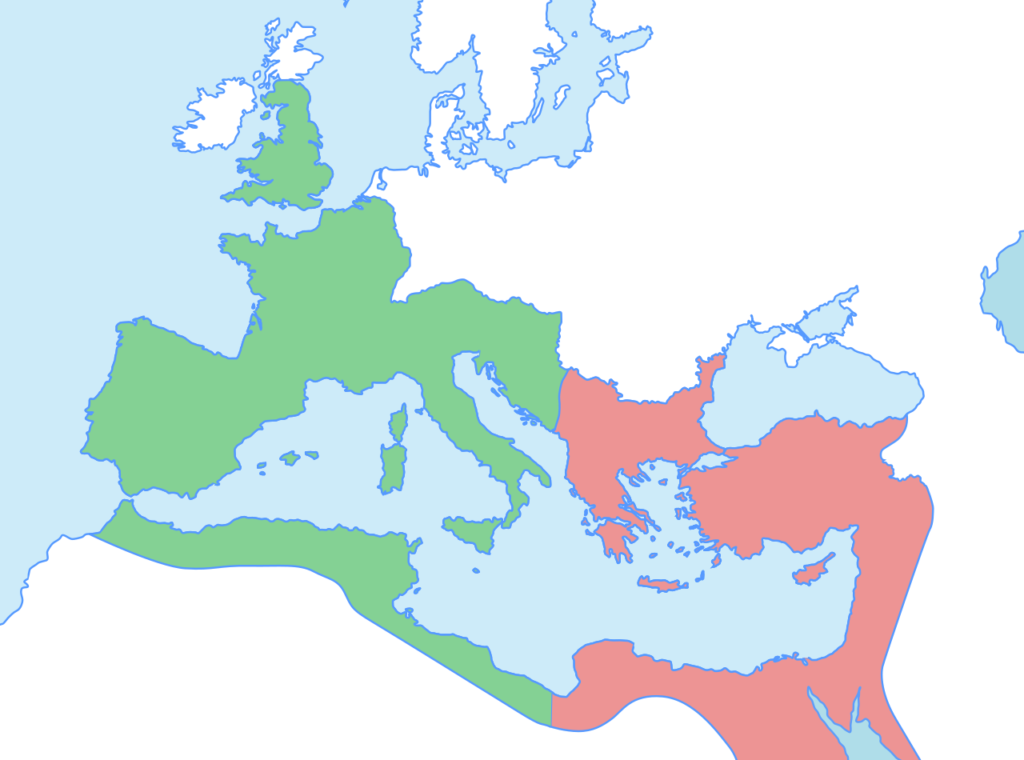
So, apparently, the Roman Empire we all study in school is the green part, the western part, the European part with its iconic boot of Italy kicking Sicily, and with the familiar shapes of France, Spain, and England facing the Atlantic Ocean. But there’s that whole red side, the less European side, the more Middle-Eastern side, which clearly includes Greece, the Balkans, Turkey, Lebanon, Syria, Jordan, Israel, Egypt, and some of Libya. Even today, that red side includes a rare fusion of diverse cultures that actually encompasses three continents—Europe, Asia, and Africa.
The author then launches into a spellbinding account of the late Roman Empire—not in its glory—but in the spasms of a violent death throe. He painted a picture of an absolute catastrophe. I still get goosebumps remembering my first impression of this tale.
Civilization had failed in totality.
Rome was sacked. Pillaging went on uncontested and tiny villages were left to fend for themselves. Barbarians migrated freely through the once secure interior of the empire. Imperial highways fell into disrepair. Stray cows milled about in the ruins of monuments, where nature crept back to reclaim the space. Roman soldiers deserted and joined the enemy. Noble families sailed out to escape their doom, only to be captured and sold into slavery. My seventeen-year-old self beheld a disaster on a scale so great that my imagination filled with epic oil painting-like scenes. And the story kept getting worse.
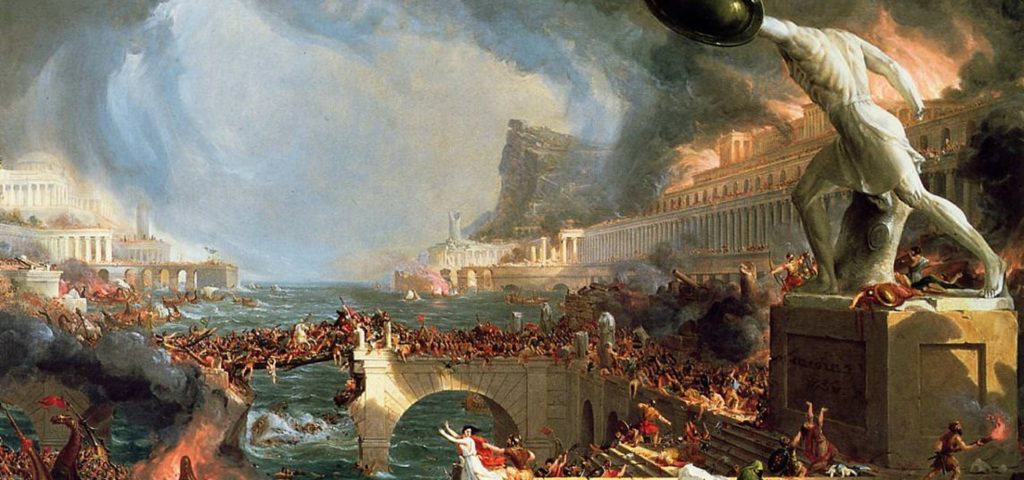

Thomas Cole’s ‘The Course of Empire’ series
Various people made radical attempts at survival in remote pockets…and failed. Desperate Roman emperors passed equally desperate policies in hopes of staving off the ruin of the empire…and failed. Finally, the black shadow of the Dark Ages truly descended upon a world that had actually lost the ability to function or even exist. I was amazed at such a thorough regression of a flagship human civilization.
In one quick stroke, my study hall that day shattered everything I thought I knew about the Roman Empire, of Western civilization. My belief that history represented steady upward progress fell short. I never considered that we could regress so decisively.
But in the East, on the side of the world we rarely talked about in class, I suddenly discovered that half of the Roman Empire survived. That “red section” had a history of its own, and it deviated quite a bit from the Roman Empire I understood.
The eastern empire was a second, bizarre Roman Empire, divorced from Europe, which didn’t even include the ancestral capital of Rome. The citizens spoke mostly Greek, not Latin. They were Christian, not pagan. They were the former conquered provinces, not the founding homeland. And from the ashes of the fallen western empire, I discovered that this eastern Frankenstein remnant of the Roman Empire would come to be known as the Byzantine Empire. These people and their empire would come to dominate the Medieval Era as the superpower of the world, exploding in culture, influence, and art.

OLYMPUS DIGITAL CAMERA
The Byzantines had little in common with the Dark Age barbarism and stagnation occurring in Europe. Moreover, the Byzantine Empire would go on ‘surviving’ for over a thousand years, making it one of the longest-lived civilizations ever.
I was so enchanted by the world I found in those pages that I pretended to lose the library book rather than return it. I paid the $18 lost fee and proceeded to horde this book my whole life.
In these pages, I met a beautiful cast of historical figures I’d otherwise never heard of, heroes and heroines who called themselves Roman but wore Asian or Russian-looking gowns and gaudy bejeweled crowns. I discovered a Byzantine general, named Belisarius. He was Justinian’s prime general and is considered a military genius. He’s considered one of the top military minds in all human history. See for yourself. Google ‘top 100 generals of all time.
(http://www.worldhistoria.com/the-top-100-generals-of-history_topic124028.html
Again, to my shock, I learned something that I never heard about in school. Remember that colorful map above, half-green and half-red? Well, Belisarius manages to reconquer the entire green section, single-handedly reuniting the Roman Empire for a generation. Impossible to believe! The civilized world fought back against the barbaric dark age.
I also read about a peasant named Petrus, who left his pig-farming village in modern Macedonia to go on to become arguably the greatest Byzantine Emperor in history. He takes on the name of his adopted father and becomes Justinian.
And then there’s his wife, Empress Theodora, whom history has never been more uncomfortable acknowledging. She had been a lowly prostitute, well known for her infamy in the seedy entertainment districts of Constantinople. She was essentially a medieval stripper and sex performer, who goes on to become a powerful intellectual contributor to Byzantine law and culture. Theodora’s undeniable influence on a sweeping legal overhaul represents some of the first Western laws designed specifically for the betterment of women and directed by a woman. The body of laws she influenced, the Corpus Juris Civilis are considered to be among the founding documents of the Westen legal tradition.

Mosaic of Empress Theodora in St. Vitale (Ravenna, Italy)
So, that one book opened me up to all of these aspects. This wasn’t the Dark Ages of Europe. This was a golden age of Byzantium. Sometimes, learning about Byzantine history feels like I’m unearthing a deep historical secret ala The Da Vinci Code or the lost city of Atlantis. And this is made all the more maddening that so few know much about it.
And yet history is incomplete without the Byzantines. For example, I was always told that Western Europe just kind of ‘woke up’ from the Dark Ages. But that’s simply not true. The Italian Renaissance began as the last generation of Byzantines made their way into Europe to escape subjugation. They brought with them their Greek culture, their literacy, legalism, and ideas. It’s well documented that the Renaissance has an unmistakable flair for Greek revivalism and that’s because of the Greek-speaking Byzantines. Within the next few decades, the Protestant Reformation began against the Catholic Church, to whom the Orthodox Byzantines had always been a rival.
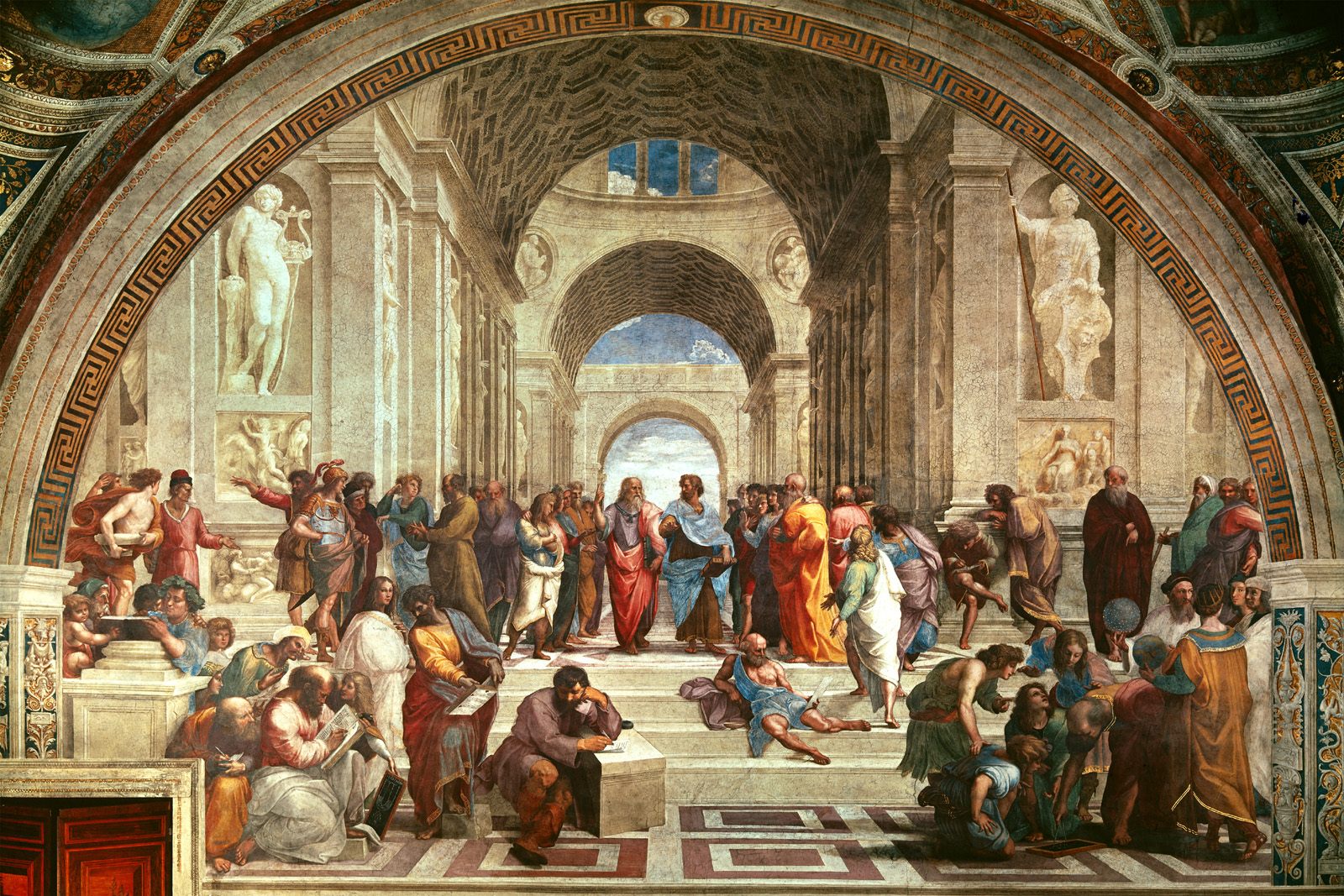

Raphael’s Renaissance painting ‘The School of Athens’
Secondly, the Turks captured Constantinople in 1453. This closed the trade routes from Europe to Asia. Did you know that the fall of the Byzantine Empire is the exact event that sent desperate European explorers across the Atlantic to find the New World? This obviously led to the Western discovery of America in 1492, a mere 39 years after the Byzantine Empire vanished from the map. Talk about shock waves. These are rapid geopolitical developments that literally set the stage for the modern world.
Thirdly, Saint Peter’s Basilica and the Vatican are considered the center of Christendom. But this is a relatively modern development. While Rome has always been central to the Christain world, Constantinople had Christianity’s greatest church, the Hagia Sophia. The great church still exists today but has since been converted into a mosque and museum in modern-day Istanbul. I’ve been there. I’ve seen it. And wow! It’s pretty spectacular for a building built 1,500 years ago. Constantinople fell to the Turks in 1453 and the construction of Saint Peter’s Basilica went into rapid motion and was completed in 1506. The timing makes perfect sense if you understand the role the Byzantine Empire played in the drama.
Scholars mostly agree that the Medieval Era spanned the one-thousand years between 500-1,500 C.E. The Byzantines emerged when Rome fell in 476 C.E., and it ended when Constantinople fell in 1453. I mean, the Byzantine lifespan is the Middle Ages. Therefore, the Byzantine Empire literally bridges a misunderstood gap in time between you and me today, and our world’s most ancient societies.



Flags of the Ottoman, Hapsburg, and Russian Empire
Geographically, the Byzantine Empire merged into the Islamic Ottoman Empire, while culturally, it migrated northeast and into the Russian Empire, and geopolitically, the Byzantines became the Hapsburg Empire (the latter two even adopted the Roman-Byzantine ‘double-eagle’ on its flag). The Ottoman and Hapsburg Empires vanished in 1918, after World War 1. The Russian Empire, however, became the Soviet Union. The so-called “eastern bloc” of the Soviet Union included many of the former Byzantine states. Therefore, the mysterious lands of the Byzantines didn’t truly open up to the West again until 1991, when the Soviet Union finally collapsed. Amazingly, this is right around the time I checked out that library book that day in 1993.
So, why don’t we know more about the Byzantine Empire? I’ve never heard a good answer to this question. I’m a 43-year old man who’s still caught up in the thrill of a book I found when I was 17. I feel like an explorer who discovered a strange and exotic land, a kind of doppelganger to Western civilization as fantastic as Tolkien’s Middle-Earth, yet part of real history. Hopefully, we can finally take a look at the lost civilization that set the table for our modern age.
If you love history, I encourage you to read about Byzantium. Go down a rabbit hole or two. You just might discover a new passion too.
Douglas A. Burton is the author of the award-winning novel, ‘Far Away Bird,’ which comes out February 6th, 2020 and details Empress Theodora’s early life. The novel is available for pre-order in paperback (Amazon, Barnes & Noble) and as an amazing audiobook (Audible.com, iTunes, Author Republic). Learn more at douglasaburton.com.

Sep 2, 2019
Women’s rights are said to be a modern movement, requiring the representation of women through a codified legal system. But if so, then Empress Theodora set the no-nonsense tone more than fifteen hundred years ago. She brought an unapologetic notion of equal rights for women when she sat on the throne and influenced sweeping reforms that should stun modern readers. And I hope you’ll share my outrage and frustration at her utter lack of recognition in history.
Her obscurity is most likely due to the obscurity of the Byzantine Empire. But I also think Theodora is marginalized because of prejudices toward her early life and career. You see, before she became an empress and epic reformist, she was a prostitute and infamous exhibitionist[i]. Empress Theodora came off as a salacious novelty, a Medieval prostitute-stripper who must have slept her way to the top. Moreover, we have a handful of lewd stories that have thoroughly defamed her. The scandalous gossip [ii]of her past is handed down to us by a single male source (who despised Theodora), which no doubt stirred the imaginations of historians through the centuries. I, myself, found the lurid tales of Theodora to be shocking and off-putting when I first read them. Not quite role model material for “decent” society.
But having written extensively about her, I’m happy to say that I’m past all that now. I want the world to get past it too. Instead, we should recognize how Theodora was exploited as a young woman and how her experiences served as a backdrop for the reforms she would influence. She dared to voice the real problems that women faced when no marketplace for such ideas existed. I can’t imagine an all-male government greeting her with open arms back in the Medieval era. Even so, Theodora designed real-world solutions, defined in legal terms, and ensured that her ideas became law[iii].
And she didn’t eff around about it. For one, she attempted to protect all women indiscriminately against sexual abuse—rich and poor, free or slave, citizen and criminal.
Under Empress Theodora, rape was made punishable by death and the rapist’s property was transferred to the rape victim[iv]. This law extended to anyone who was present during the rape, regardless of position or rank. Theodora also saw to it that women could own and inherit property[v], which is quite a breakthrough because it gave daughters and wives real social power. A family’s wealth could now continue through a daughter, and should a woman’s husband die, the wife could claim the property and fortune. This greater legal status alone gave women throughout the empire real power in real terms.
Unlike today, professional outlets for women were severely restrictive. Besides the socially acceptable “work-from-home-and-raise-a-family” jobs, such as weaving, innkeeping, or baking, the very concept of ‘professional women’ as a large and recognizable class didn’t exist with one exception. A large number of women worked in theaters and brothels. So, although this professional class of women carried a huge social stigma, their industry was one of the few places where women worked publicly outside the traditional family structure and earned real income.
Therefore, laws that addressed legal matters for this lowly and socially powerless group should be seen as bold and unashamedly supportive of women in general. Theodora meant to treat the professional woman of her society, sex workers though they may be, as professionals. She understood that these prostitutes, actresses, mimes, and singers earned incomes that could technically sustain them. Income should mean independence. But brothel keepers had legal and oppressive authority over these women. So, Theodora shifted the legal authority from the brothel keepers to the prostitutes.
Under the new laws, women could no longer be forced into prostitution[vi]. If a woman willingly chose prostitution but later wished to leave, Theodora’s laws made it illegal for a brothel-keeper to stop her. And Theodora followed up relentlessly to ensure enforcement of these new laws. When Theodora discovered that brothel keepers undermined the new laws by making girls swear oaths never to leave the brothels, she responded by rendering such oaths illegal[vii]. She mandated that the provincial governor and the head bishop had the responsibility to enforce this law, giving her direct oversight over a manageable number of men in high positions. She chose two men to enforce, because if the governor, himself, blocked a woman’s departure from a brothel, then the bishop could override the governor. You see, Theodora had once been a concubine in the service of one of these provincial governors. She knew only too well the kind of power these men had over women. So, she added some checks and balances. Pretty amazing.
Theodora didn’t stop there. She helped to overhaul the marriage laws of her time. These reforms should be regarded as revolutionary since they shattered the most powerful class barriers.
For centuries, there was a ban on intermarriage between the upper and lower classes[viii]. By law, a prostitute could never marry a nobleman. Such a rigid class system was characteristic of a Roman world view and regarded high title and rank as self-evident. Secondly, even under the new Christian perspective, prostitution was regarded as immoral and sinful. Therefore, when Theodora helped to facilitate the removal of the marriage ban, she did so without the support of either secular or religious tradition. Her personal world view alone guided the legal reform. By removing the marriage ban[ix], prostitutes could now marry into noble houses and gain legal status. Like it or not, this represents unparalleled social mobility for women at the time. It gave many women access to power.
By having the marriage ban removed, Theodora, herself, was finally free to marry into the upper classes, which paved the way toward her destiny as an empress. Quite a move. She then saw to it that her sister, her daughter, and numerous other theater friends all married into noble houses. Just like that, several women crossed an impossible barrier and gained incredible social power, and they achieved this change in fortune seemingly overnight.
Once, Theodora arranged a marriage between one of her theater friends (an ex-prostitute) and a nobleman named Saturnitus[x]. When Theodora heard that this Saturnitus complained that his prospective bride wasn’t a virgin, she had the nobleman brought before her, rolled in a blanket, and flogged with a cane. She asked Saturnitus just one question: why could he frequent the brothels with impunity and dare to demand virginity from his wife? Theodora didn’t believe in double-standards.
Other laws, too, applied to all women regarding marriage. In Byzantium, there was a law of ‘mutual consent’ in divorce cases. A divorce was granted only if both the husband and the wife agreed to void the marriage. By the way, this legal concept is still practiced in some countries today. If the wife seeks a divorce, but not the husband, she stays married against her will. You might point out that this law works in both directions. However, if a man was forced to stay in a marriage because his wife vetoed the divorce, especially back then, he could easily visit a brothel or tavern and enjoy a full life outside the home. Wives did not have this luxury. (They weren’t even allowed on the street without an escort[xi]). So, the law of mutual consent worked disproportionately against women.
So, Theodora struck down the law of mutual consent.
Secondly, women of the time were expected to offer a dowry to their grooms. By Theodora’s time, the custom had expanded to make it fashionable for men to offer something minor in return. This minor offering was called an “antenuptial.’ Under the new laws, the antenuptial had to be equal to the bride’s dowry. Equal to the bride. Theodora’s message is inspiring in its consistency.
She also knew that prospective brides could sometimes be pressured into a marriage. A woman might give consent initially when put on the spot, but as the marriage date grew near, she might think differently. Therefore, a new law came out that required the prospective bride to give her consent twice—once at the original proposal, and then again before the marriage took place. This allowed women to change their minds before entering into a lifelong commitment[xii].
Finally, in what I regard as a remarkable example of Theodora’s scope, sympathies, and real-world knowledge, she even dared to protect criminal women. In the Sixth Century, legal protection for male criminals was unheard of. That’s why I regard Theodora’s intervention on behalf of criminal women to be truly groundbreaking. If a woman required prison time, the new laws forbade her imprisonment in common jails where she had no protection from male guards who could abuse these women without recourse. Criminal women had zero voice in government. Well, until Theodora. She saw to it that criminal women were removed from common prisons and detained in a Nunnery (that she constructed), under the supervision of other women.
Empress Theodora was known to hold court in her opulent imperial bedchamber. The sight must have been spectacular. There, surrounded by a retinue of her most trusted women and eunuchs, Theodora ruled over what has been described as an almost “parallel government[xiii].” Many women (and men) came directly to Theodora to plead for justice, and the formidable empress meted out justice with purpose. To me, this bizarre audience chamber is a Sixth Century attempt at giving women representation and a voice. The scene in Theodora’s bedchambers mirrored the actual throne room of the Byzantine Empire, just a few hundred feet away. In the words of James Allan Evans, “In the eyes of the upper-class beholder, what Theodora represented was revolutionary.”
Theodora’s mark on history is a powerful, immovable example for us. The body of laws that came into being during her reign is known as the Corpus Juris Civilis and, according to Wikipedia: “The Corpus continues to have a major influence on public international law. Its four parts thus constitute the foundation documents of the Western legal tradition[xiv].” Uh, wow. If this is true…if the Corpus is at the heart of the Western legal tradition, then Theodora is at the heart of a womens’ tradition toward equal rights. Official credit for the Corpus goes to Emperor Justinian, and he deserves plenty of it. But no historian can doubt Theodora’s powerful presence in the laws that pertain to women.
History, it seems, remains uncomfortable with Theodora’s sexualized past but I think we’re missing the point. Instead of judging Theodora for the slanderous stories, we should recognize that she was part of an institutionalized system that exploited women. I see a direct and significant connection between her early life and the legal reforms she oversaw as an empress. Our culture is taking a second look at history and rediscovering the contributions of women throughout the ages. I say, look further eastward, beyond Europe and deeper into the past. In my view, Theodora is the real deal. She stands tall among the women of history and it’s time the world recognizes her accomplishments in full.
Douglas A. Burton is on a mission to introduce Theodora to as many people as possible. His upcoming novel, ‘Far Away Bird,’ which details her early life, comes out February 6th, 2020. To read a brief excerpt, click here: Excerpt 1 (Training to be an informer). And if you liked the article, please share it.
[i] The Secret History, Procopius [9. p15]
[ii] The Secret History, Procopius [9. p15]
[iii] The Empress Theodora: Partner of Justinian p. 37
[iv] Codex Justinianus [Book IX Title 13]
[v] Novellae 5.2 cf. Evans (1996a), pp 209-10
[vi] Codex Justinianus [I.4.33]
[vii] Novellae 51
[viii] The Empress Theodora: Partner of Justinian p. 37
[ix] Codex Justinianus (Book V Title 4-23)
[x] The Secret History, Procopius [17. p24-26]
[xi] Constantinople: Birth of an Empire
[xii] The Emperor Justinian and the Byzantine Empire p. 27
[xiii] Theodora: Empress of Byzantium p.175
[xiv] Wikipedia ‘Corpus Juris Civilis’

Jun 19, 2019
For 25 years I’ve read about the Byzantine Empire. Now that I’m writing this journal, I realize that very few people have ever asked me why, and how I became so passionately intrigued by the Byzantines. Only a few of my closest friends and family members know about my unusual side passion. Even they don’t ask “why” anymore. Reading about Byzantium was just something I did on my own, in private, while leaving little trace evidence in my regular life. It’s a niche fascination that rarely found its way into regular conversations. Whenever I do end up mentioning something about the Byzantine Empire, or that the capital was Constantinople, the most common response I get (and I’m not kidding) is a pause and then a cheery rendition of Istanbul Not Constantinople. So now it’s Istanbul, not Constantinople, and we all get that.
But how did this particular time and place in the world come to capture my imagination so entirely? Like many things for me, the culprit was a book.
I can actually tell you the exact day my fascination with the Byzantine Empire began. It was on March 10th, 1993. I know this because the library card is still inside the book cover to this day. The book was a non-fiction work called, Constantinople: Birth of an Empire by Harold Lamb, and it was published way back in 1957. During my 1993 study hall, though, I just needed a book to kill time because I sure as hell wasn’t going to do my Algebra homework. So, I flipped through the pages, and the musty scent of old paper really set the tone. There were some black & white pictures on a few pages depicting a mosque-like building of some kind, various mosaics, and stone reliefs. I turned back to the first page and started reading:
The author opens with:
This is the story of a city built by survivors. As often happens in a great disaster, these survivors were not one people ethnically, but a fusion of many peoples. They gathered together to defend not so much their lives and property as their way of life. In so doing they displayed a certain perversity; they refused to surrender their city. They kept on refusing for nearly a thousand years. History has named them the Byzantines…
So, wait a minute, I thought. This sounds nothing like the Roman Empire I learned about in any schoolroom. The Romans were of one people ethnically, you know, the Romans, so this account baffled me. The Roman Empire was a civilization built not by survivors, but by conquerors.
The author goes on:
They were alone in their survival. In the West, a long twilight fell on the Roman Empire during the centuries between A.D. 200 and 450. It ended in the darkness of the first Middle Age. In the East, however, the inhabitants of this city learned the hard lessons of disaster, and they managed to hold back the night.
Images of invincible Roman legionnaires, of architectural splendor, and ancient decadence all seemed at odds with the rather morbid tone the book struck. What the hell was this guy talking about? I flipped to a map in the index and got a better idea. The Roman Empire had been split in two at some point, a west and an east empire. I remembered hearing something about the split, but then also realized that I never heard about what happened to that eastern portion of the empire. It was like the weird old uncle you meet at a family reunion and never hear from again.
Here’s what I’m talking about:
So, apparently, the Roman Empire we all study in school is the orange part, the western part, the European part with its iconic boot of Italy kicking Sicily, and with the familiar shapes of France and Spain leaning into the Atlantic Ocean. But there’s that whole purple side, the less European side, which clearly includes Greece, the Balkans, all of Turkey, parts of Asia, the entire Middle-East, Egypt, and Libya. Even today, that purple side includes a rare fusion of diverse cultures that actually encompasses three continents—Europe, Asia, and Africa.
The author then launches into a spellbinding account of the late Roman Empire—not in its glory—but in the spasms of a violent death throe. He painted a picture of an absolute catastrophe. I still get goosebumps remembering the tale. Civilization had failed in totality. Rome was sacked. Pillaging went on uncontested and tiny villages were left to fend for themselves. Barbarians migrated freely through the once secure interior of the empire. Imperial highways fell into disrepair. Stray cows milled about in the ruins of monuments, where nature crept back to reclaim the space. Roman soldiers deserted and joined the enemy. Noble families sailed out to escape their doom, only to be captured and sold into slavery. Like the final hour of the movie Titanic, I beheld a disaster on a scale so great that my imagination was paralyzed. And the story kept getting worse. Various people made radical attempts at survival in remote pockets…and failed. Desperate Roman emperors passed equally desperate policies in hopes of saving the empire…and failed. Finally, the black shadow of the Dark Ages truly descended upon a world that had actually lost the ability to function or even exist. I was amazed at such a thorough regression of a flagship human civilization.
But in the East, on the side of the world we rarely talked about in class, I suddenly discovered that half of the Roman Empire survived. That purple section had a history of its own, and it deviated quite a bit from the Roman Empire I understood. A man named Constantine won a civil war and became a Roman Emperor. He saw the writing on the wall that the Roman Empire was in dire straits. He built a city from scrap in the year 324 C.E. and turned the small fishing village of Byzantium into the City of Constantine, a sister capital of a Roman Empire. The eastern empire was a second, bizarre Roman Empire that was divorced from Europe and didn’t even include the ancestral capital of Rome. The citizens spoke mostly Greek, not Latin. They were Christian, not pagan. They were the former conquered provinces, not the founding homeland. And from the ashes of the fallen Western Empire, I discovered that this eastern Frankenstein remnant of the Roman Empire would come to be known as the Byzantine Empire. These people and their empire would come to dominate the Medieval Era as the superpower of the world, exploding in culture, influence, and art. They had little in common with the Dark Age and barbarism occurring in Europe. Moreover, the Byzantine Empire would go on ‘surviving’ for over a thousand years, making it one of the longest-lived civilizations ever. It lasted until the year 1453.
In one quick stroke, my study hall that day shattered everything I thought I knew about the Roman Empire, of Western civilization, and my belief that all of history represented steady upward progress. I never considered that we could lose it all and even regress.
I was so enchanted by the world I found in those pages that my 17-year old self, in all his wisdom, pretended to lose the library book rather than return it. I paid the $18 lost fee and proceeded to horde this book my whole life.
In these pages, I met a beautiful cast of real-life people I’d otherwise never heard of, heroes and heroines who called themselves Roman but wore eastern, almost Asian-looking gowns and gaudy bejeweled crowns. In my 20’s I was mostly captivated by a young Byzantine general, named Belisarius. He was Justinian’s prime general and is considered a military savant. In his early 30’s, he goes on to accomplish some military feats that are so amazing that he’s still considered one of the top generals in all human history. Google ‘top 100 generals of all time.’ Click on the first link, and you’ll find him under the Medieval Era. Click on the second link, and you’ll find him ranked #9 all time, etc. Again, to my shock, I learned something that I never heard about in school. Remember that colorful map I included above? The one with the half orange, half purple Roman empire? Well, Belisarius manages to reconquer the entire orange section, including the old capital of Rome, herself. And for a generation, the entire Roman Empire was united once again, a truly impossible thing to believe. The battles he fought made him a poster child of a civilized world that fought back now against the hordes of barbarian armies, outnumbered, yet winning in the most ingenious ways. Civilization made a comeback under the command of General Belisarius.
Can you imagine…sixty years after the tragic fall of Rome…the sight of a Roman army marching through the Tuscan hills, returning after all these years to liberate the mother city of Rome from barbarian rule? For the Roman villagers who came out to see for themselves, Belisarius and his troops must have looked like apparitions from a time long forgotten. The image captivated me. How come I never heard about any of this before?
I also read about a peasant named Petrus, who left his pig-farming village in modern Macedonia to go on to become arguably the greatest Byzantine Emperor in history. He takes on the name of his adopted father and becomes Justinian. And then there’s his wife, Empress Theodora, whom history has never been more uncomfortable acknowledging. She had been a lowly prostitute, well known for her infamy in the seedy entertainment districts of Constantinople. She was essentially a medieval stripper and sex performer, who goes on to become a powerful intellectual contributor to Byzantine law and culture. Theodora’s undeniable influence on a sweeping legal overhaul may indeed represent the first official laws designed specifically for the betterment of women, and directed by a woman. The only reason why Theodora isn’t a household name is probably because we don’t know much about the Byzantines. I’ve never been able to forget this generation of historical people and I’ve always dreamt of writing about them.
So, that one book opened me up to all of these aspects. This wasn’t the Dark Ages of Europe. This was something entirely new. The Byzantine Empire should not have existed. It shouldn’t have gone on as long as it did. Belisarius, Justinian, and Theodora should never have accomplished what they did, given their lowly origins. To me, they were historical superheroes and I, alone, seemed to know their feats.
My library is now filled with 45 books on the Byzantine Empire. Some of my books are out of print and are considered quite rare. Sometimes, learning about Byzantine history feels like I’m unearthing a deep historical secret ala The Da Vinci Code or even the lost city of Atlantis. And this is made all the more maddening that nearly no one knows much about it.
Here’s a fun little test. Name a movie, television show, or novel that has the Byzantine Empire as a setting. No, really, name one.
I mean, we have movies set in ancient Greece, Ancient Egypt, Rome, Medieval Japan, Medieval China, South America, the Mayan Empire, Antarctica, Middle-Earth, Mars, and Tatooine. And yet, I bet you cannot come up with a single relevant story set in the Byzantine Empire. Seriously. Why?
History is incomplete without the Byzantines. For example, I was always told that Western Europe just kind of ‘woke up’ out of the Dark Ages. But that’s simply not true. Western Europe awoke only once the “brain drain” of Byzantine intellectuals migrated to Europe when Constantinople was captured by the Turks. This bizarre eastern culture was the very catalyst that set modern history into motion.
Constantinople finally fell in the year 1453. If you Google ‘The Italian Renaissance’ you’ll see that it began in roughly 1420, at the exact time that the last generation of Byzantines made their way into Europe to escape subjugation. They brought with them their Greek culture, their literacy, legalism, and ideas. It’s well documented that the Renaissance has an unmistakable flair for Greek revivalism and that’s because of the Greek-speaking Byzantines. Within the next few decades, the Protestant Reformation would begin against the Catholic Church, to whom the Orthodox Byzantines had always been a rival.
Secondly, the closure of the trade routes to India, which went through Constantinople, is the exact event that sent desperate European explorers across the Atlantic to find a new trade route. This obviously led to the Western discovery of America in 1492, a mere 39 years since the Byzantine Empire disappeared. Talk about shock waves. These are rapid geopolitical developments that literally set the stage for the modern world in which we now live.
Thirdly, if I asked anyone today, “where is the capital of Christendom?” They’d say, “the Vatican.” And if I asked, “what is the name of the great church at the heart of the Vatican?” Most people would answer, “Saint Peter’s Basilica.” But did you know that Saint Peter’s Basilica, as we know it, didn’t even exist during the entire medieval era? The modern Vatican that tourists visit year-round is merely a modern adaption of its medieval predecessor. The Byzantine Empire had been the face of Christendom on earth in the medieval world and a great church, known as the Hagia Sophia (look it up if you get a chance), had been the great monumental church for all of Christianity. The great church still exists today but has since been converted into a mosque in modern day Istanbul. I’ve been there. I’ve seen it, and wow. It’s pretty spectacular for a building built in 536 C.E. So, when Constantinople fell to the Turks, Christianity no longer had a great church. Only when Constantinople faced certain doom to the rival religion of Islam, did the need arise for a new ‘big’ church. The construction of Saint Peter’s Basilica went into rapid motion and was completed in 1506. The timing makes perfect sense if you understand the role the Byzantine Empire played in the drama.
Did you know that the Corpus Juris Civilis (which was a Byzantine contribution under Theodora and Justinian) is a cornerstone of modern Western law, including the legal system of the United States? Wikipedia even says: “The Corpus continues to have a major influence on public international law. Its four parts thus constitute the foundation documents of the Western legal tradition.” What? That’s huge! An incredible amount of Western civilization is in debt to the never-mentioned, barely-heard-of Byzantines.
Finally, Google ‘The medieval era’ or better yet, ‘History by period.’ Both searches will show the same thing. You’ll see that history is divided up into three main categories. There’s the Ancient Period or Antiquity. There’s the Postclassical or Medieval Era, and there’s Modern History, which is essentially the last 500 years. All of human history is under the umbrella of these three categories, and these are pretty standard date ranges among scholars. The Medieval Era spanned the one-thousand years between 500-1,500 C.E. The Byzantines emerged as a truly independent civilization when Rome fell in 476 C.E., and it ended when Constantinople fell to the Turks in 1453. I mean, the Byzantine lifespan is the Middle Ages. Therefore, this culture’s very existence on earth represents a singularly unique epoch in human history. The Byzantine Empire literally bridges a misunderstood gap in time between you and me today, and our world’s most ancient societies.
Geographically, the Byzantine Empire essentially merged into the Islamic Ottoman Empire, while culturally, it migrated into the Eastern Orthodox Russian Empire, and geopolitically, it became the Hapsburg Empire (which still used the Roman ‘double-eagle’ on its flag). The Ottoman and Hapsburg Empires vanished in 1918, after World War 1. The Russian Empire, however, had a revolution at that time and became the Soviet Union. The U.S.S.R. came to occupy what we call ‘Eastern Europe,’ which clearly matches up with many of the former Byzantine states. Therefore, the mysterious lands of the Byzantines didn’t truly open up to the West again until 1991, when the Soviet Union finally collapsed. Amazingly, this is right around the time I checked out that library book.
Most of our perception of the Byzantines is found indirectly with our fascination with the eastern European mystique. We see it in stories like Bram Stoker’s Dracula, which takes place in Romanian Transylvania and has an occultic Byzantine feel, or Agatha Christie’s Murder on the Orient Express. We see the Hagia Sophia in movies like From Russia with Love, The International¸ or Tom Hank’s Inferno. And most recently, Millennials walked on the streets of 16th Century Constantinople in the critically acclaimed video game, Assassin’s Creed: Revelations. But none of these things quite explain the forgotten super culture that once tied them all together.
So, why don’t we know more about the Byzantine Empire? I’ve never gotten a good answer to this question. I’m a 42-year old man still caught up in the thrill of a book I found when I was 17. I feel like an explorer who discovered a bizarro world, a kind of doppelganger to Western civilization as exotic and fantastic as Tolkien’s Middle-Earth. And now, I’d love to share this world with anyone who’s willing to listen.
Carl Jung
“What does the example of the Roman Empire teach us? After the conquest of Asia Minor, Rome became Asiatic, even Europe was impacted by Asia and remains so today. Out of Selecia came the Mithraic cult, the religion of the Roman Army and its spread from Egypt to fog bound Britain. Need I point to the Asiatic origin of Christianity? We have not yet clearly grasped the fact that Western theosophy is an amateurish imitation of the East.”
Mar 24, 2019
Writing my book fundamentally changed me. In my effort to understand my lead heroine, Theodora, I uncovered a range of human experiences that were unfamiliar to me. The more I learned, the more I changed. The three central questions I get are why did you try to write from a woman’s perspective? What made you focus on such a sensitive issue? And what qualifies you to even write about this particular subject matter? I’m going to answer all three questions because the answers will also shed light on how I, myself, changed during my writing of the book.
So, why write from a female perspective? I didn’t see this as a particularly unusual matter, especially since there are plenty of women who’ve written male lead characters. But I guess it’s a curious question anyway. Back in 2009, I wrote, or attempted to write, a Byzantine novel written in the first person with Emperor Justinian as my main character. I wrote a whopping 500 pages and got lost in the woods. I never set up my major plot lines correctly, nor did I introduce important characters that would prove pivotal to the plot and climax. In short, I needed to learn more about story structure. I vowed to one day return and rewrite my Justinian epic, armed with the mysterious knowledge of story structure.
Over the next seven years, I broke down all my favorite movies—Star Wars, Amadeus, Silence of the Lambs, The Matrix, Aliens, Avatar, etc. I read Joseph Campbell’s The Hero with a Thousand Faces. I read all the great historical novels such as The Grapes of Wrath, For Whom the Bell Tolls, To Kill a Mockingbird, The Far Pavilions, Ben Hur, Gone with the Wind, and, yes, even War and Peace. After reading Memoirs of a Geisha, though, I wondered for the first time if Theodora, an actress-prostitute (and notorious exhibitionist), could work as a possible competing story line alongside my Justinian story. Perhaps I could portray the life of a Byzantine prostitute similar to the fascinating Japanese geisha I’d just read about. I wondered whether readers might find it interesting to see a future famous empress in this light. But I decided firmly against the idea because Theodora presented some unique problems. For one, showing a great female leader as a salacious prostitute instead of focusing on her accomplishments as an empress could be a really bad idea…worse than you think…
Let me explain.
There is an account of Empress Theodora’s early life that is so salacious that even I, despite admiring her historically, have struggled to reconcile. In what may be one of the greatest acts of gossip and defamation in history, the Byzantine historian, Procopius, tells a story of Theodora that has followed her through the centuries, a story regarding her portrayal of Leda and the Swan. No one reading or learning about Empress Theodora can be spared this story from her early life. I’ll let you read it for yourself. Here’s the X-rated excerpt from Procopius’ best-known work, The Secret History:
Often in the theater, too, in full view of all the people she would throw off her clothes and stand naked in their midst…she would spread herself out and lie face upwards on the floor. Servants on whom this task had been imposed sprinkle barley grains over her private parts, and geese trained for the purpose used to pick them off one by one with their bills and swallow them. Theodora, far from blushing when she stood up again, actually seemed to be proud of this performance. For she was not only shameless herself, but did more than anyone else to encourage shamelessness.
And Procopius goes on to say:
Never was anyone so completely given up to unlimited self-indulgence. Often she would go to a bring-your-own-food dinner-party with ten young men or more, all at the peak of their physical powers and with fornication as their chief object in life, and would lie with all her fellow-diners in turn the whole night long: when she had reduced them all to a state of exhaustion she would go onto their servants, as many as thirty on occasion, and copulate with every one of them; but even so she couldn’t satisfy her lust.
Procopius goes on and on. Even ‘fans’ of Theodora have to wince and wish they hadn’t read that. Check it out. Wikipedia mentions Leda and the Swan. It’s probably just gossip, but how could I possibly include Theodora’s early life and avoid this utterly unflattering story (along with all the other stories)? Even if I tried to ‘skip’ these accounts, readers would eventually discover them and any ‘untainted’ character portrayal of Theodora would risk collapse. Better to double down on Justinian’s story, and leave Theodora out of the book altogether.
But something happened to change my mind.
Based on a recommendation, I happened to be reading an utterly unrelated non-fiction book called Revolt of the Elites. I wasn’t even thinking about my unwritten Byzantine novel. Near the end of his book, the author attempts a deep-reaching analysis of politics and went into what seemed like a bizarre segue. He cites the work of a psychoanalyst, named Leon Wurmser, who published case studies on female exhibitionism. The psychoanalyst concluded that some of these women battled a deep inner shame and overcame the shame through acts of shamelessness. It’s a form of what’s called ‘counterphobia’ in which people engage excessively in something they fear as a defense mechanism. Here’s the exact passage I read regarding modern case studies:
…her fear of defilement and dishonor made her wish to defile others—a striking illustration of the connection between shameful disgrace and the shameless act of exposure. Another patient wished to hide her face from the world—the characteristic stance of shame—but also had a compulsion to exhibit herself. It was as if she were saying, “I want to show the world how magnificently I can hide.” Here, the rage for exposure was redirected to the self, in the form of an exhibitionism that “knew no shame,” as we used to say.
On the one hand, these patients wanted to see everything, as if they hoped to merge with the world through the medium of the eye. On the other hand, they wanted to dominate the world by making themselves objects of universal fascination. Fearing exposure, they wore the frozen, expressionless face Wurmser came to recognize as the mask of shame: “the immovable, inscrutable, enigmatic expression of a sphinx.” Yet this forbidding countenance served, in their fantasies, not only to hide their own secrets but to fascinate and dominate others, to punish others, as well, for attempting to penetrate their facades. The self-protective mask of shame was also the magically aggressive face of Medusa, which turns onlookers to stone.
By mentioning exhibitionism and shamelessness, I immediately thought again of Theodora and her early life as a “notorious” prostitute and exhibitionist. Did she fit this psychological profile? What if Theodora’s historical infamy was actually due to a childhood trauma? What if the trauma made her so ashamed that she engaged in excessive exhibitionism to overcome the trauma? What if she was actually suffering underneath the whole time? And what if overcoming the childhood trauma was the very thing that helped her become one of the greatest empresses in Byzantine history? Whoa. That seemed like a pretty big character arc.
I renewed my idea of a competing story line for Theodora. I always listen to music as part of my creative process. So, I was listening to this piece and an image popped into my head, an image of a young girl with her back to me. She was kneeling and praying alone in a medieval Byzantine basilica, not long after enduring a terrible abuse. She needed answers. She needed to know why. And she needed to understand why the world favored her rapist over her. These were rather brutal questions, but they resonated with me. That single image made me sympathize with the girl in my mind in a rather powerful way. It set in motion a glimpse of the path for Empress Theodora. The story would explain her salacious past in a new light, and at the same time offer an explanation as to what she had to overcome in order to become the stuff of empresses. It also explained why, after she became an empress, she made rape punishable by death, and why she helped to bring about dozens of laws designed specifically to help women. (She may have even been the first woman ever to truly act in a way consistent with a modern notion of women’s rights.)
In fact, now…instead of shying away from the lurid stories about Theodora, what if I confronted them head on? What if I left nothing out? What if I showed all her most defaming moments in the context of a woman who is attempting to brazenly DESTROY her inner shame at what happened to her? These questions stalked my mind for weeks. I also considered—in my loftiest daydreams—that if my book was ever actually successful, I could reverse the effects of Theodora’s 1,500-year smear campaign. People would know her worst stories, but instead of losing respect for her, they would see a heroine and an actual historical figure.
That’s why I wanted to write about a woman and that’s how the sensitive topic became central to the story.
I wrote out a few pages that tried to capture Theodora as a character and found myself immersed in her realities. I had terrible emotional reactions to the writing. But the more I wrote about her and her situation, the more engaged I felt. I even decided to drop my original plot line with Justinian entirely and to focus all my attention on Theodora.
But am I qualified to write about such abuses? The answer in my mind was a resounding “definitely not.”
Rape, abuse, and sexual assault are big and forbidden topics, especially for a guy without firsthand knowledge to be writing about. I feared (and still fear) that I’d become an unwelcome guest in a conversation that I had no business getting into. Clearly, I wasn’t including rape as a plot device—I saw it as the most likely causal event if the aforementioned case studies were to be believed. A sexual assault could easily create an unbearable shame that could force a girl to reinvent herself as sexually aggressive. It fit Wurmser’s psychological profile. So, I made the decision to be courageous and just write. But I challenged myself to get this right, to the best of my abilities.
I did have some things to draw upon. I have a cousin who experienced sexual abuse when she was very young, and I had a friend who was abused repeatedly by his older brother, and he, in turn, to his younger brother. Years before, both of them shared details and accounts about their experiences, even though I was extremely uncomfortable hearing these things at the time. I circled back to what they told me…I was listening now. The stories they had told me, though, didn’t always match the portrayal of rape I’d seen in movies, etc.
In movies, rape is often portrayed as a violent assault by an aggressive man or group of men. But, the more I read up on true accounts of rape, I discovered that many rapes occur by someone the victim trusted and in a way that was murkier, less obvious to the victim, often because they were young, inexperienced, or dealing with a man of high social status—social, professional, or even within a family.
In these scenarios, I learned that sexual attackers can create what I called a “confusion of consent.” The rapist attempts to convince or seduce the victim rather than risking a violent assault. In many cases, even the victim is left with some ambiguity, whether self-imposed or not, as to what actually happened. Obviously, blatant assaults occur too, but I found the seductive elements to be more horrible in a certain way, because the rapist inflicts a kind of persistent psychological residue that leaves the victim forever confused. The subtle assault is less obvious. Many victims can remember participating consciously or unconsciously in some kind of a lead up to the assault. Other times, victims were blindsided with improper requests by a person of high status. And once the rape takes place, victims are unlikely to speak out because of the powerful and oppressive “confusion of consent.” The waters are muddied. And if the rapist has any kind of high social status, then whatever benefits or favors the rapist is providing— both to the victim and indeed to all those who benefit from the rapist’s position—would be on the line if the victim were to challenge. The victim risks angering everyone and so finds an impossible circumstance of powerful social resistance to their tiny and unwanted claim to justice. This, too, started to hurt me just by trying to comprehend it. And I mean it. The injustice was quite large and would be in place and functional in any culture, in any time period, regardless of the moral norms. The motivation of the rapist would always be there and social nature of human beings would always establish a natural resistance to true resolution.
So, after understanding Theodora’s situation a little better, I had to turn to my villain. I have to get him right too. I learned why films portray male rapists as merely violent. Because as a writer, you cannot dare to give any redeeming qualities to such a man. He must be obviously evil and all evil. But I felt that readers needed to feel the nature of the subtle traps, since possibly, these were the most common traps. So, my villain would be a man of higher social status. My villain would hide in plain sight. He would be especially skilled at creating the “confusion of consent,” and he could deliver certain favors or benefits to Theodora that would make her question any challenge to him. He would deliver favors and benefits to many other people who surrounded Theodora. So, worst of all, the other people in Theodora’s world recognized and valued the social significance of her rapist and would become unexpected enforcers against her desire to challenge. No one will help Theodora challenge this villain, even if they knew what he did to Theodora. By challenging the villain, Theodora would become the villain to others. I felt certain that the villain I was about to create was real, and I knew this person existed around the world in many forms.
I also thought it was important to know who Theodora was before the assault. I had a feeling I knew this girl too. She’d have a positive self-image. She’d think highly of herself. She’d be optimistic and capable. She’d be smart and her ability to succeed would make her willing to take risks. And her innocence would allow her to completely underestimate the villain.
As I wrote about Theodora, I realized that I related to her in other ways. In my own life, I learned that when something really bad happens to you, people really don’t want to hear about it. They avoid you. You become an unwanted guest, viewed as toxic or negative. Wanting to talk about an injustice is bothersome. This part of her story I shared with her. I once lost everything and so, I knew also the sting of a social estrangement, a social collapse.
There were mornings, when after I wrote about Theodora, I’d go up for a shower, look in the mirror and see that my face looked pale. I felt heavy and constricted. I was uneasy for entire days. Trying to enter the head space of Theodora absolutely crushed my spirits sometimes. I’m not embarrassed to admit, there were many days that I cried. I’d get stuck in a stage of anguish from the leftover feelings of writing certain scenes or moments. My eyes were red and people could tell that I’d been crying. If I felt that bad after simply writing about these awful things, then I truly shuddered to imagine any human being who actually experienced this situation firsthand.
The time came for me to beta test my story, to come forward and allow strangers to read the pages I’d written in private about Theodora. My wife encouraged me to be brave about it. To my utter horror, I discovered that my writer’s group were all women. I had one question. When would they all turn against me for my clumsy foray into a room clearly marked “women only?”
To my utter surprise and extreme relief, every woman in that group had my back. They were supportive and engaged. They provided absolutely vital feedback in areas where I was still blind. These women helped me to understand my own lead character even better. And then, one of the writers informed me privately that she had actually experienced a rape in her recent past. That’s when it hit me: this shit’s real. The whole thing I’d been torturing myself trying to articulate was right up close. Real people I cared about were telling me about it. This woman offered to answer any questions I had, which I thought was unequivocally brave. She explained certain things to me, terrible and true details that I would have never known about, things that led me to grasp even more of the reality. Some of my more introverted writing peers left me feedback as well, peculiar feedback that led me to suspect they, too, had some experience with abuse, direct or through a friend, even if they didn’t outright tell me.
When a close friend of our family came over one night, a wonderful, witty, confident girl we’d known for years, and heard about my novel, she too, confessed that she’d been abused as a young girl. Suddenly, my cousin and old friend weren’t isolated stories from my past. The number of women with stories of abuse was getting uncomfortably crowded. And in an impossible coincidence of timing, the #MeToo movement struck in 2017 and my writing topic was now being echoed on national television. This signaled a devastating confirmation that abuse was indeed widespread and was occurring to women of all colors, all classes, all shapes, and sizes.
Suddenly, I saw how my conceptual “confusion of consent” could work on anyone, even the wealthy…even the strong ones. in fact, in what I deem as a truly awful paradox, women with high confidence and a strong self-image could actually see these positive qualities work against them…because a confident woman might not allow herself to acknowledge the awful truth of abuse. How could a high self-image exist side-by-side with a victim scenario? It sets up a perfect situation for self-denial. That actually made sense to me. That explained how a high-profile actress, CEO, or any successful woman could end up tweeting #MeToo. And then when I think about girls (or even boys) with lower self-esteem…I know in my heart that their desire or willingness to challenge their attacker would be reduced to an awful mode of silence.
So, yes, writing this book has had a big impact on me. I learned a terrible truth. That’s why I’ve chosen to go forward with this book on my own. While a child version of myself hopes for success, I care mostly about people getting something out of my story. I want others to experience a similar understanding to a problem that exists today, even if they, too, weren’t looking for it. I want people to learn about and be fascinated at Empress Theodora, because she’s a great woman in history. I believe she’s been obscured in history because the Byzantine Empire is obscured.
Circling back to the conception of the novel, I found again the passages by Procopius that I quoted earlier. He defamed Theodora for the last 1,500 years by telling us stories that shock and unsettle us when we think of Theodora. But, I challenge Procopius. I didn’t shy away from his slanderous description of Theodora. During the climax of my book, I actually have one of my characters speak aloud Procopius’ exact words, reconstructing the passage as dialogue, and setting the words one more time against Theodora directly. I put the defamation out there for all to hear and let the readers judge for themselves whether a sexualized woman is always guilty.
There is a fatalism to our greatest heroes and heroines. They dare where we recoil. I believe that this daring comes from losing a fear of death. In many ways, acts of evil kill the human spirit; they create a living experience not unlike death, right here in this world. That’s why, I guess, I believe heroes are tragic figures, even when they triumph, because sometimes, to triumph is to know that something like death has already visited them. Both the wound and healed scar are hidden from our eyes and so we see only their uncharacteristic bravery.
Theodora changed me for sure. I understand that the Hero’s Journey (or Heroine’s Journey in this case) is not such a glamorous thing if you let it all in. I learned about my own world and about problems that haven’t changed much whether we’re in the Sixth Century or the Twenty-First. I learned what #MeToo means on some deeper level. And I hope, if all goes well, that something as simple as a book can start conversations, thoughts, and solutions about what might solve the problems at hand. That’s why I’m willing to donate part of any profits from the book to a non-profit such as RAINN or the Joyful Heart Foundation.
So, that’s my tale as it relates to the sensitive subject matter of my book. There’s plenty more to the book and to Theodora, of course, but these issues seem to be at the heart of people’s curiosity and relevant to modern readers.



















